Update Since 0.3.0, most class and function names have been updated according to pep8.
Days ago when I published the first version of pymasker for masking Landsat 8 image, Dr. Robert A. Washington-Allen suggested me whether the package would be used for MODIS products. After I read technical documents of MODIS, I realize that the Quality Control bits of MOIDS products has the same structure as the QA band of Landsat 8. Therefore, I update the package to adapt MODIS products (or other NASA products with similar QC/QA bits).
In this article, I am going to show how to extract masks from the Quality Control bits of MODIS land product in python.
MODIS QC/QA bits
The QC/QA bits of MODIS is a binary number, of which each section represents the state of certain condition. Just take the 250m resolution land surface reflectance product (MOD09GQ) as example. The QC band (maybe called QA band in other products) is the fourth band of the HDF dataset. It is a unsigned 16-bit band. Each value on the pixel indicates a combination of pixel conditions. We can interpret the value by separating its binary form.
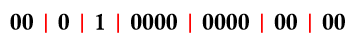
The individual bits within a binary number are read from let to right as described in the following table.
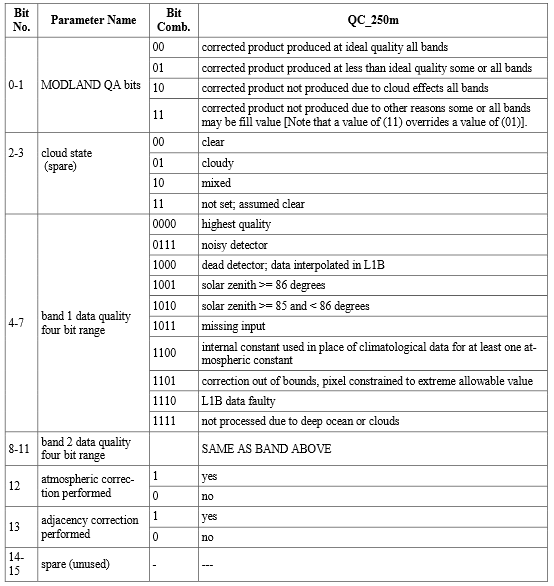
Therefore when we put the interpretation back to the bit string, we are able to know what it indicates.
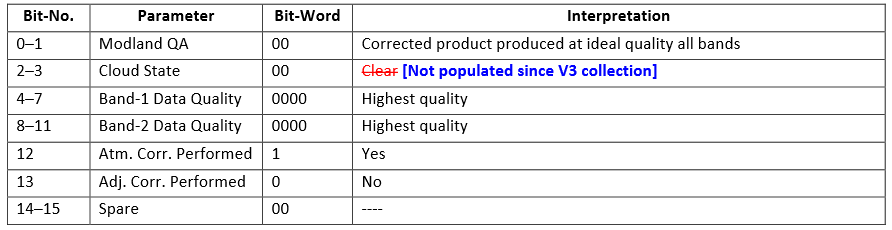
As this binary number is 4096 in integer, all pixels having value 4096 in the QC band are high quality and cloud free with atmosphere correction, but no adjacency correction.
The structure of QC/QA bits vary in different MODISO products and different data collection. For full detail for each product, please have a look at
In the next sections, I will show how to make masks based on the QC/QA bits in python.
Preparation
Before getting started, you need to do the following preparations:
Download and install pymasker.
Know the band number of QC/QA band in your HDF dataset.
Know the QC/QA bit structure of your dataset. If you only want the mask of quality level, you don’t have to know the bit structure. Please go bottom and read the new update.
Maksing for MODIS product
I will continue to use MOD09GQ in the sample. First you need to load the QC Band
1 | from pymasker import Masker |
You need to know the bit information to generate certain masks. For example, we want a mask only wit high quality pixels. In the previous section we have known that the quality bits start at the beginning (position 0) and the length is 2. We also know that ‘00’ indicate corrected product produced at ideal quality in all bands. Therefore, the high quality mask could be made with
1 | # Get high quality mask |
Then you can get a binary mask where 1 represents the high quality pixel.
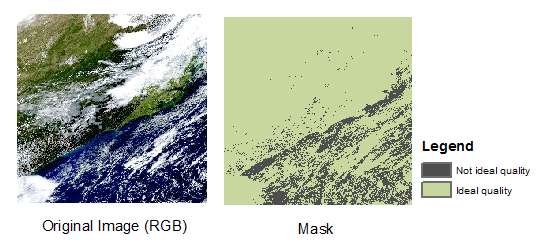
Update
Pyamsker has provided a new class for producing QA mask since version 0.2.2. So you don’t have to look for and remember those binary bits (Well I don’t like them, too).
I have wrapped quality levels for MODIS land products.
1 | from pymasker import ModisQuality |
Therefore, the masking code would be very intuitive and readable.
1 | # Create a MODIS QA masker, similar to creating a masker above |
I am going to gradually support all MODIS products in the future release. Please look forward to my new update :)